Broadening the History of Science
October 12, 2021
The National Science Foundation awards history professor Karin Rosemblatt a $400,000 grant.
By Jessica Weiss ’05
Students of science in the United States are likely to recognize the names and discoveries of Sir Isaac Newton, Galileo and Charles Darwin. Fewer may know of the many influential curanderos, cosmologists and agriculturists from across the Americas whose work has impacted science across the globe for centuries.
Thanks to a $400,000 grant from the National Science Foundation, a new project led by Professor of History Karin Rosemblatt aims to establish how Latin America’s popular, Indigenous and Afro-descendant communities were “never on the periphery of scientific developments.”
“We aim to shift emphasis away from the discoveries of a few scientific geniuses and to foreground instead the many contributors to scientific work—porters, local guides, wives and family members, technicians, herbal specialists,” said Rosemblatt, who is also the director of UMD’s Nathan and Jeanette Miller Center for Historical Studies.
The project, “Placing Latin America and the Caribbean in the History of Science, Technology, Environment, and Medicine,” will bring together senior and established researchers and graduate students in the field of HSTEM (History of Science, Technology, Environment and Medicine) in Latin America and the Caribbean. The network will secure ties among researchers in North and South America, produce publications that make their research widely available and provide training and mentoring to graduate students.
Rosemblatt, whose research focuses on the transnational study of gender, race, ethnicity and class, has already coordinated a 13-person steering committee made up of scholars at different stages of their careers working in Latin America and the United States. The committee members specialize in different time periods, geographic regions and topics. They include: Miruna Achim (Universidad Autónoma Metropolitana-Cuajimalpa, Mexico City); Eve Buckley (University of Delaware); Marcos Cueto (Oswaldo Cruz Foundation, Rio de Janeiro); Sebastián Gil-Riaño (University of Pennsylvania); Pablo F. Gómez (University of Wisconsin-Madison); Carlos López Beltrán (National Autonomous University of Mexico); Camilo Quintero (UNIANDES, Colombia); Megan Raby (University of Texas at Austin); Julia Rodriguez (University of New Hampshire); Carlos Sanhueza Cerda (Universidad de Chile); Elisa Sevilla Perez (Universidad de San Francisco, Quito); and Adam Warren (University of Washington, Seattle). Ana Luísa Reis Castro (MIT) will serve as graduate student representative.
Next steps involve growing the network and building out a website.
Through the materials produced by the network, teachers of students of all ages will also gain access to bibliographies, lesson plans, essays and collections of syllabi that allow them to cover a broader range of scientific endeavors and a more diverse community of scientists, Rosemblatt said.
“We hope to convince other historians, students and the broader public that the Western scientific tradition developed in conversation with other, often colonized, peoples,” she said.
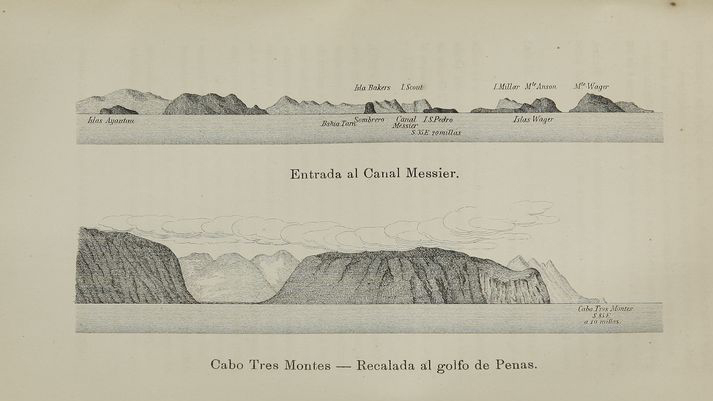
Image: “Two views of Cabo Tres Montes” (Chile), 1891, via memoriachilena.cl.